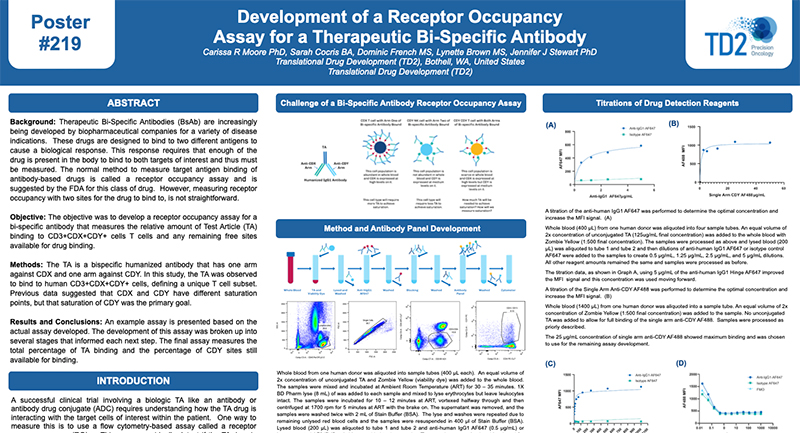
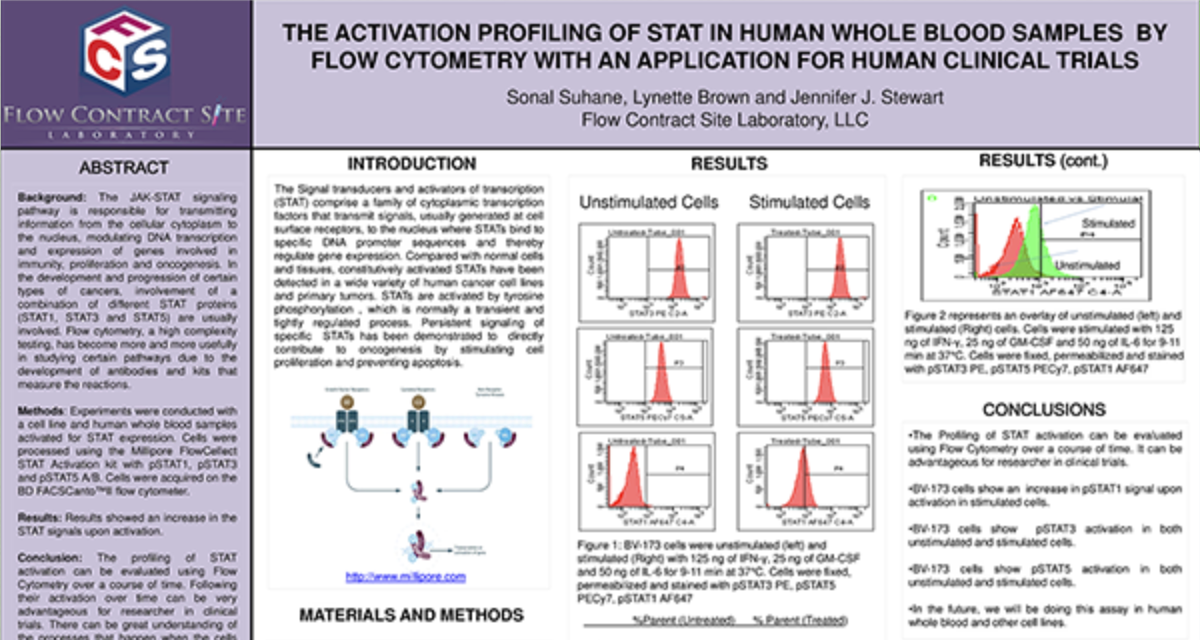
Functional Assays
We have full service cell culture capabilities to demonstrate whether or not a cell has the capacity of performing certain functions. Currently we have assays to evaluate Natural Killer Cell Cytoxicity Assay and a Basophil Activation Test (BAT). Please inquire to start the scientific discussion.
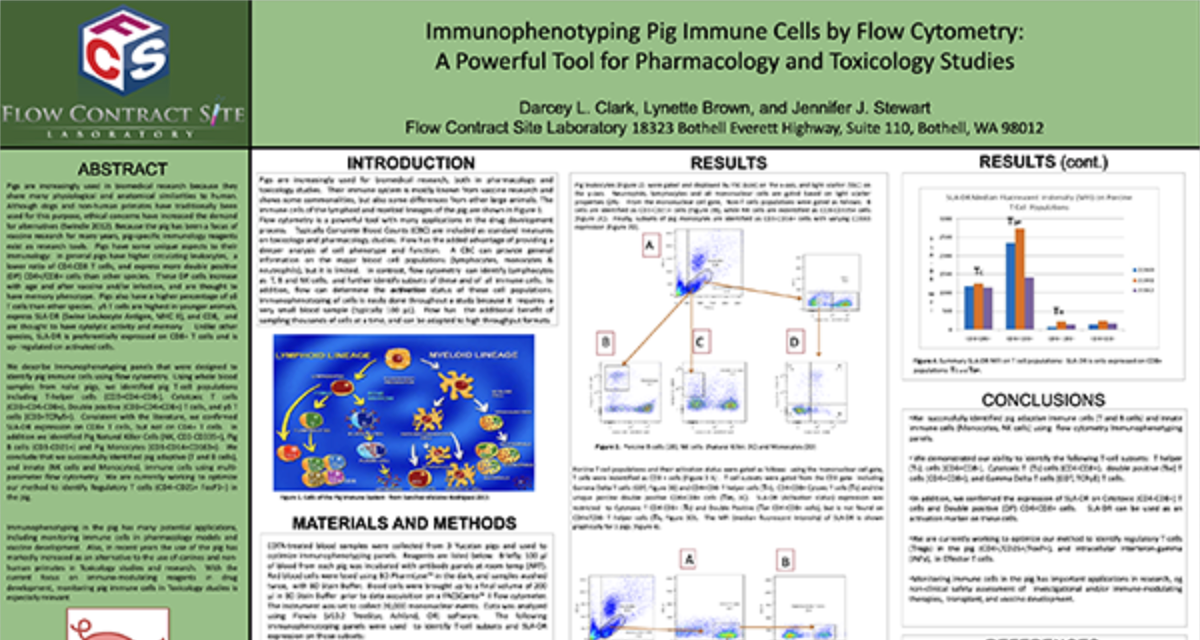
NK cytotoxicity assay: We have developed and offer a flow cytometry based NK cytotoxicity assay to evaluate human and non-human primate NK cell effector function. K562 target cells are labeled with PKH67 (a fluorescent green dye that labels the cell membrane) to discriminate target cells from effector cells. Then, effector cells (PBMCs) are incubated with the PKH67 labeled K562 target cells at different Effector to Target (E:T) cell ratios from 100:1, 50:1 and 25:1. After co-culture, the cell mixtures are stained with 7-AAD (7-Aminoactinomycin D) which is a fluorescent chemical compound with a strong affinity for DNA used to detect dead cells (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Schematic representation of the interaction of PKH67 labeled K562 target cells with NK effector cells in PBMC.
The percentages of 7AAD positive (dead) K562 target cells are determined by flow cytometry at each Effector to Target (E:T) ratio tested. A comparison of NK cell cytotoxicity in human and Non-Human Primate (NHP) in the presence or absence of IL-2, a cytokine which can enhance NK cell effector function. In addition to evaluating NK cytolytic activity, each donor can be immunophenotyped for their NK cell number.

Figure 2. Ratio of Effector: Target cells (E:T) vs the % Cytotoxicity of human and NHP NK cells. Human and NHP NK cytolytic activity is highest at the 100:1 E:T ratio, with a dose-dependent decline as the E:T ratio decreases. IL-2 enhances both human and NHP NK cytotoxicity.
Request more information about Functional Assays
Contact our experts to help advance your drug development with TD2's trusted Flow Cytometry Services.
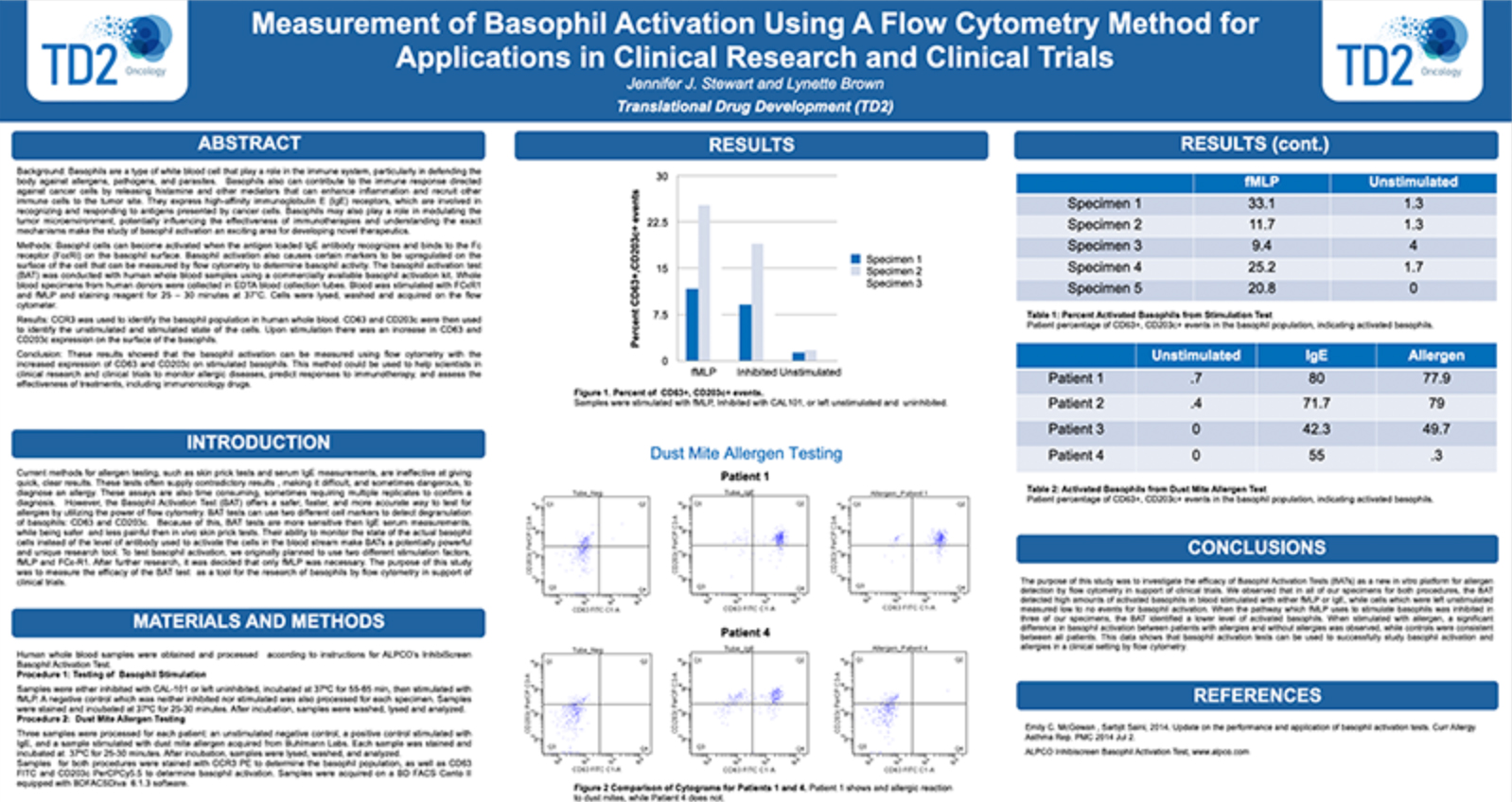
Basophil Activation Test (BAT): FCSL offers the Basophil Activation Test for research and clinical applications. BAT is currently used for the evaluation of various allergic conditions, such as environmental allergens, food allergens and drug allergies including the assessment of clinical response to allergen-specific immunotherapy and other immunomodulatory treatments. The BAT offers an easy in vitro assay to test patient sensitivity to various substances prior to the initiation of clinical trials.
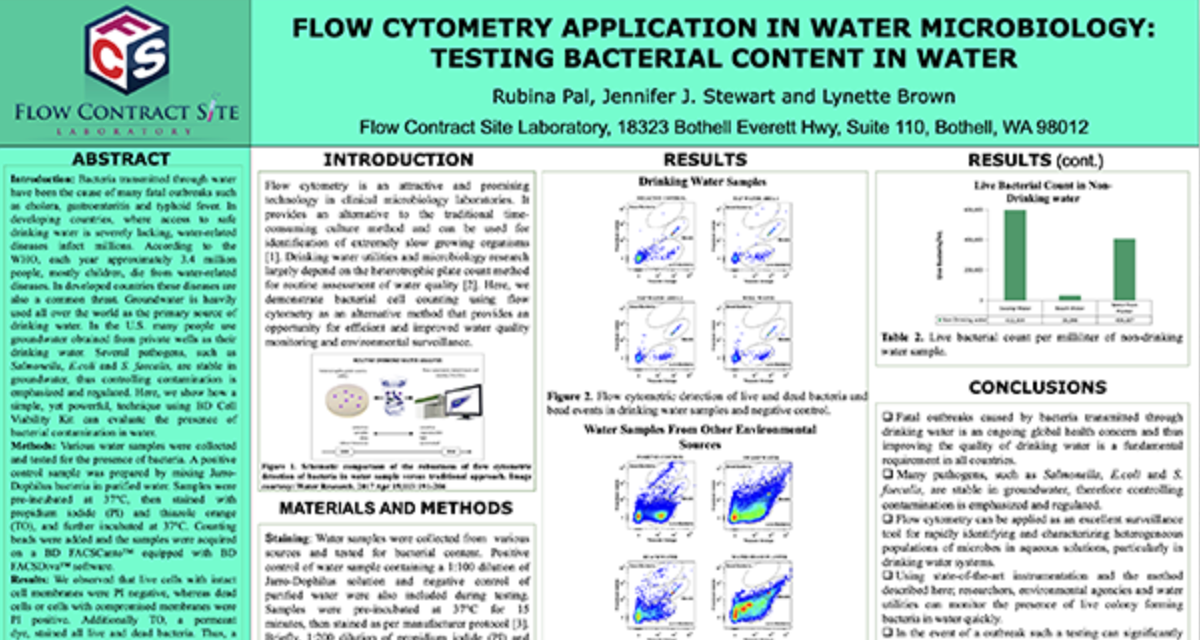
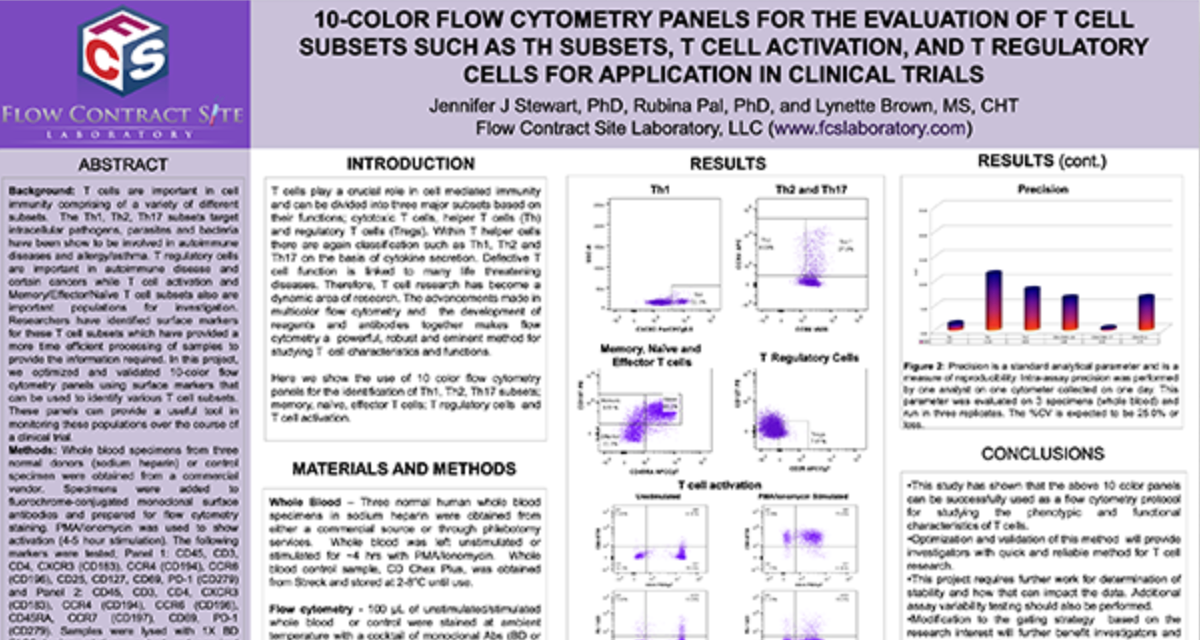
To test the reliability and efficacy of the BAT at FCSL, we performed a qualification study using a commercially available basophil activation kit (Flow CAST®, Buhlmann). Blood samples were incubated under 3 separate conditions: unstimulated, stimulated with fMLP (N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine, a positive control for basophil degranulation) and stimulated with dust mite allergen. Each sample was stained for CCR3 (a basophil identification marker) along with CD203c and CD63 (basophil activation markers) during incubation. After incubation, red blood cells were lysed, and the samples washed and analyzed using a flow cytometry with results shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. Top Panel (A) Basophil surface marker changes with allergen encounter include up-regulation of both CD63 (LAMP3) and CD203c (ENPP3). CD63 is a found on membranes of intracellular vesicles and is only exposed on the cell surface with activation and degranulation. Bottom Panel (B) – Histogram overlay comparing the expression of CD63 on the surface of unactivated basophils (orange) to samples that have been activated by exposure to antigen (purple). Bottom Panel (C) – The evaluation of dust mite antigen for two subjects, Patient 1, has clear dust mite allergy while Patient 2, is negative for dust mite allergy.
For more information on how we can help you to evaluate NK function or basophil activation in non-clinical and clinical studies or evaluate your drug for its effect on cellular function please inquire to start the discussion.
Additional Resources
GET STARTED
Work with a team who believes in your research as much as you do.
Are you ready to start your Flow Cytometry studies? Partner with a collaborative oncology CRO that believes in your treatment as much as you do. Take the first step today and contact our experts.
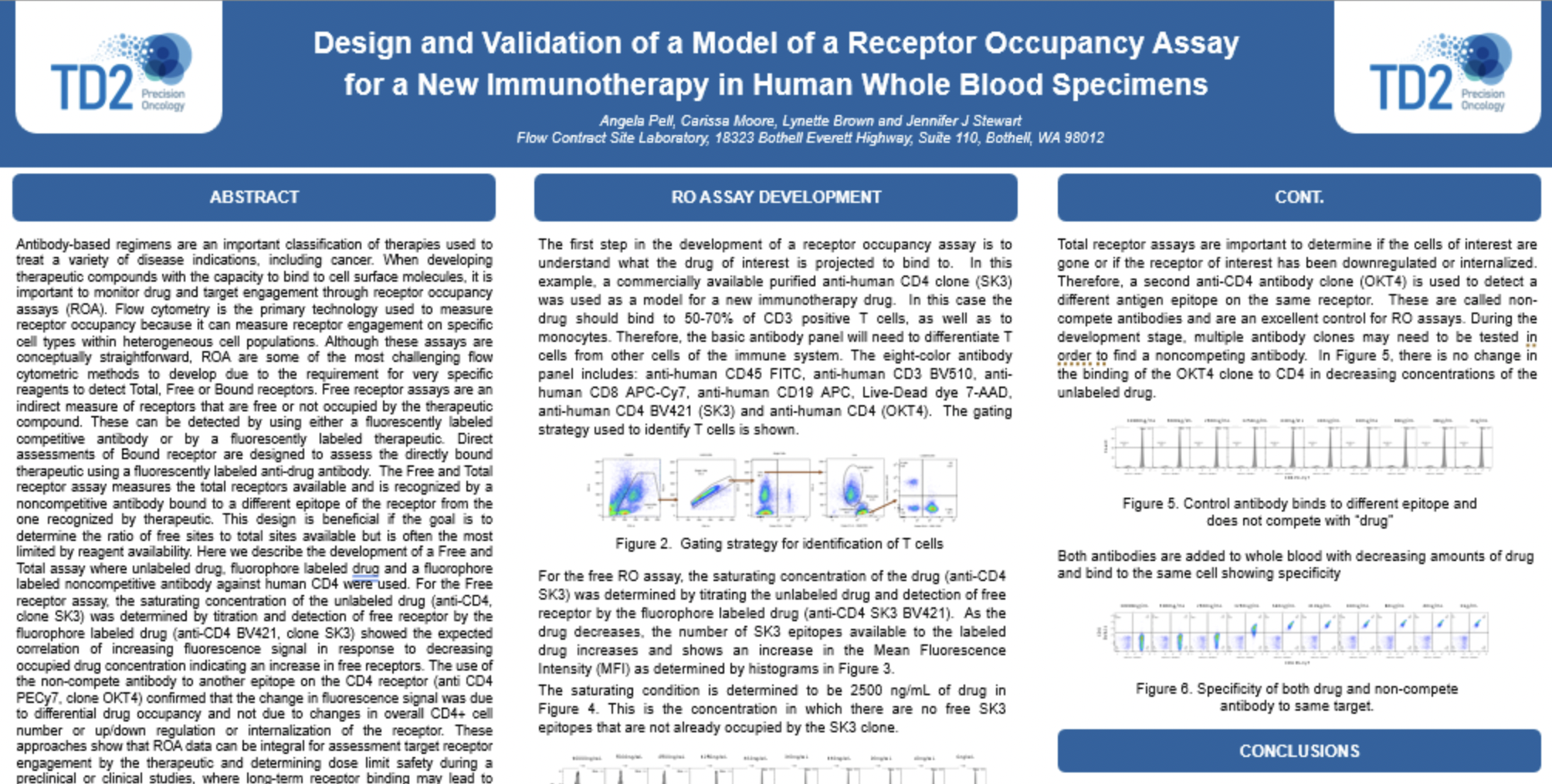
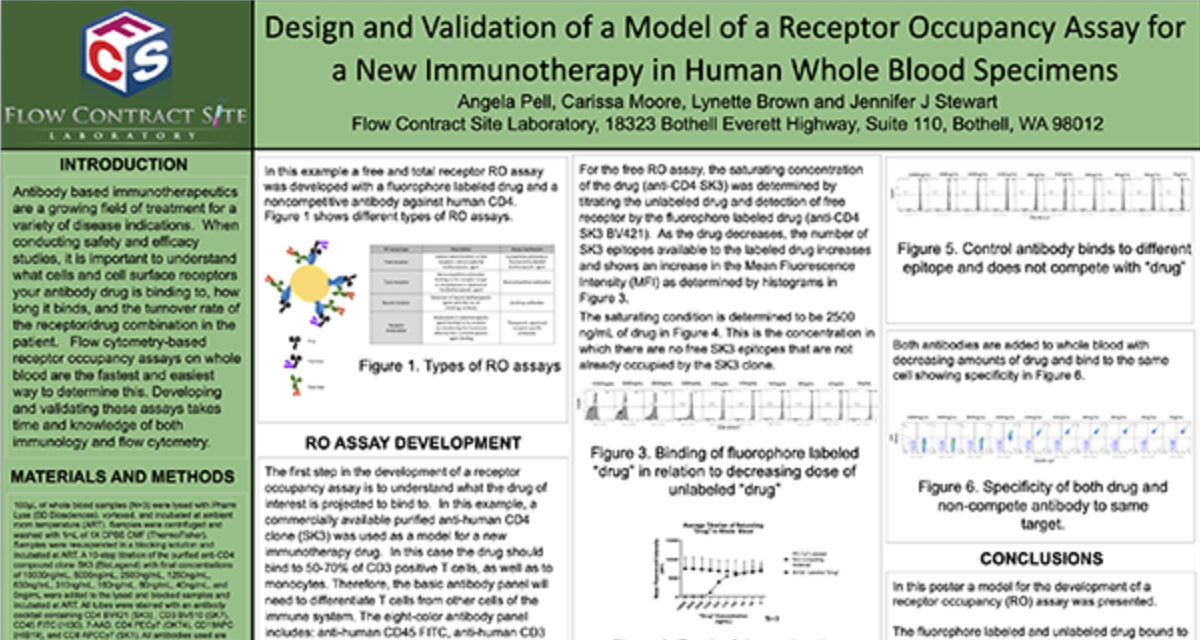
![]() Receptor Occupancy
Receptor Occupancy
Binding of fluorophore labeled “drug” in relation to decreasing dose of unlabeled “drug”

![]() Receptor Occupancy
Receptor Occupancy
![]() PBMC Services
PBMC Services
Evaluate responses of PBMCs by profiling the function/phenotype of subpopulations

![]() Immune Population Phenotyping
Immune Population Phenotyping
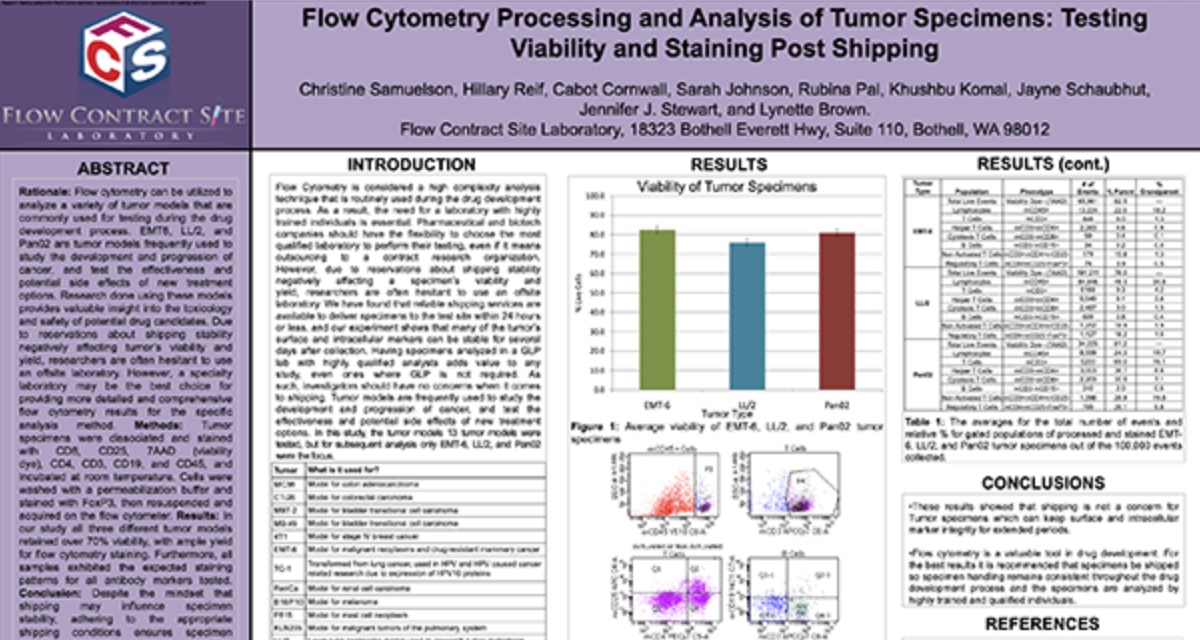
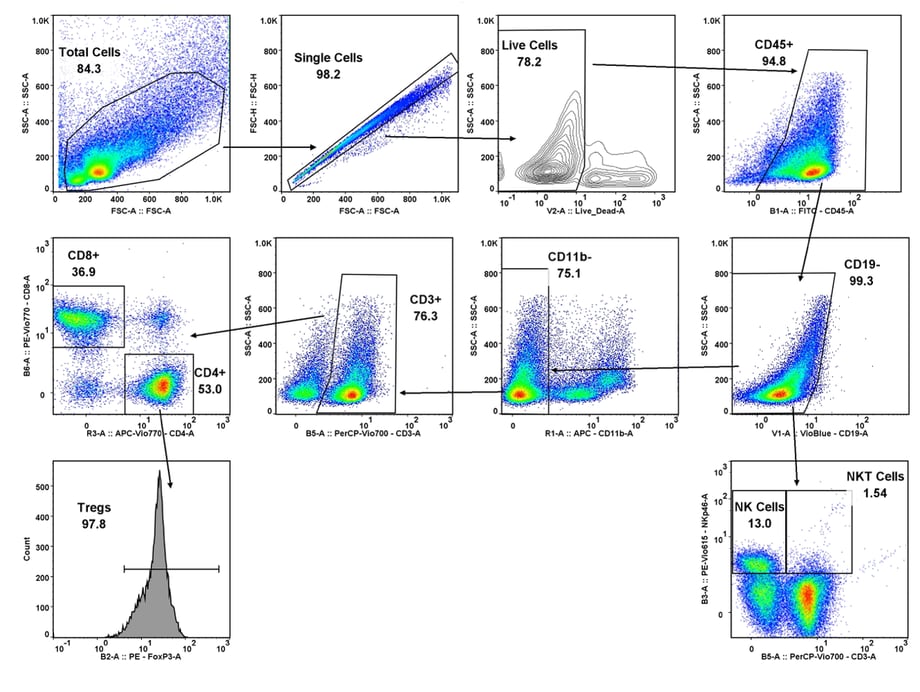
Immune cell population analysis of subcutaneous CT26 murine colon carcinoma tumors
CT26 SC tumors: Gating strategy T cells and NK cells.
Gating involved identifying the total cell population, and then gate out the doublets, gate out the dead cells, move on to our first marker CD45 which gates out any non-immune cells. The bottom right cytogram shows the different NK cell populations. The far left middle cytogram depicts the two T cell population CD4+ and CD8+. Values are % of total CD45+ cells.
![]() Cancer Cells/Tumor Specific Marker Expression
Cancer Cells/Tumor Specific Marker Expression
Cancer cells/tumors specific markers expression
- Viability dye inclusion
- Cell lines and single-cell suspension tumors
- Surface staining

![]() Fluorescent Proteins Expression
Fluorescent Proteins Expression
Fluorescent proteins expression
- Viability dye inclusion
- Cell lines and transfected primary cells
- Surface staining

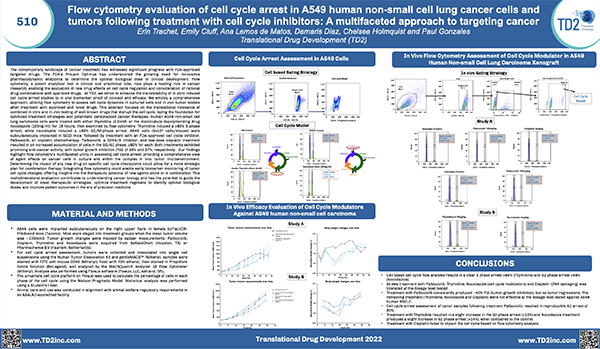
![]() Cell Cycle Analysis
Cell Cycle Analysis
Cell cycle analysis A549 cells
- Propidium iodide
- Cell lines

![]() Intracellular Protein Analysis
Intracellular Protein Analysis
- Intracellular Cytokines
- Phosphorylated Proteins
- T-Regs
- Phosphoroteins
- Cytokines

![]() Cellular Functional Assays
Cellular Functional Assays
- NK Cell Function
- Basophil Activation Test (BAT)